LISTS
Lists are mutable datatype in python. Python lists are containers to store values of any datatype.
LIST SLICING
How to get character of a given index in a list in python
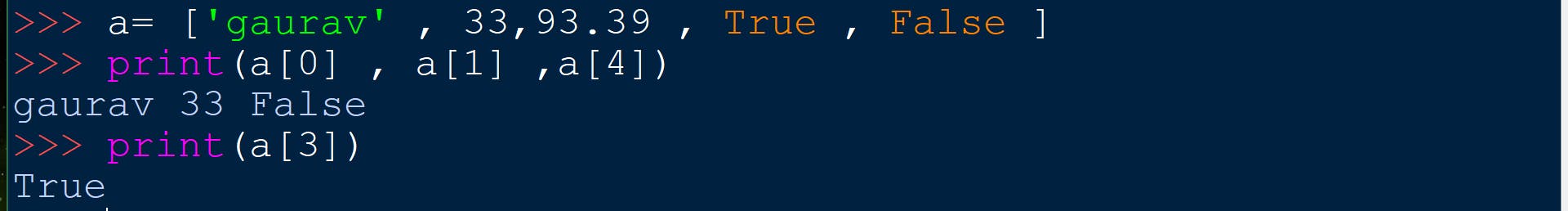
How to slice a given list.
SYNTAX - name_of_variable[start : end : stop]
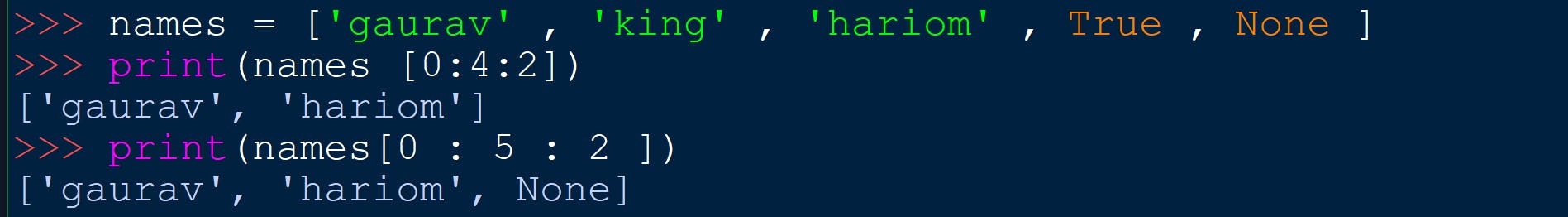
NOTES -
If nothing is written in place of start , then the function will start slicing from the index = 0
If nothing is written in place of end , then the function will do slicing till the end of the string.
If nothing is written in place of step , then the function will print every character.
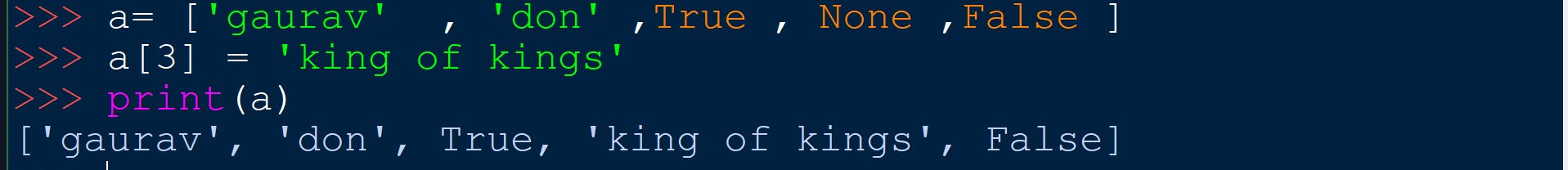
NOTE -> We can access the characters of a list and also change them using this function . But we cannot do this in strings because strings are immutable datatype in python but lists are mutable datatype in python.
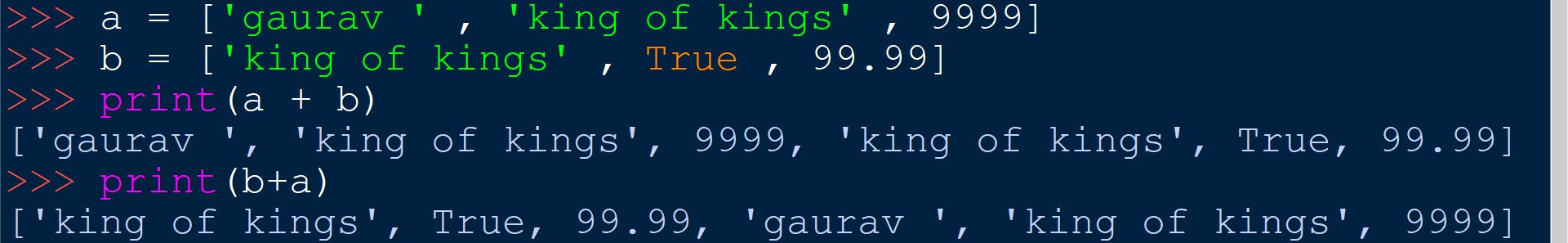
CONCATENATION OF LISTS
LIST METHODS
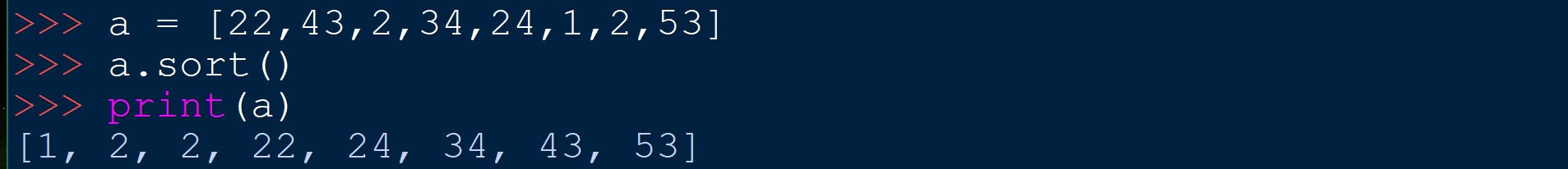
name_of_list.sort()
It sorts the values of the list in ascending order.
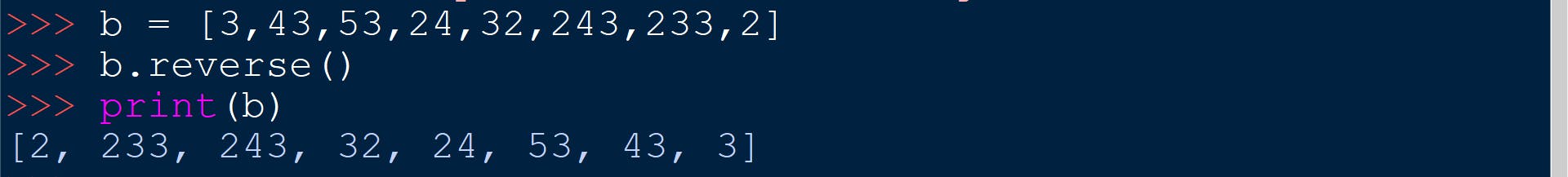
name_of_list.reverse()
It reverses the order of elements in the given list.
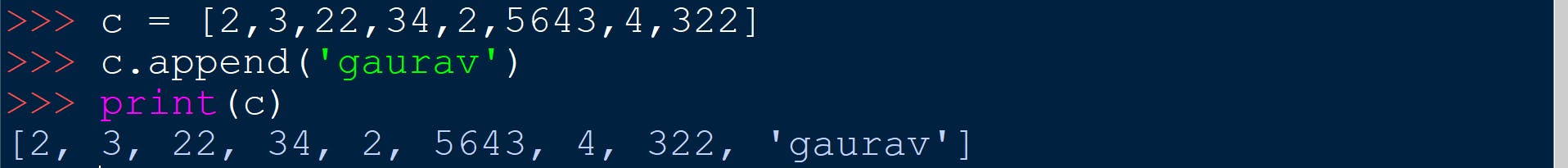
name_of_list.append(x)
Adds the given item at the end of the list.
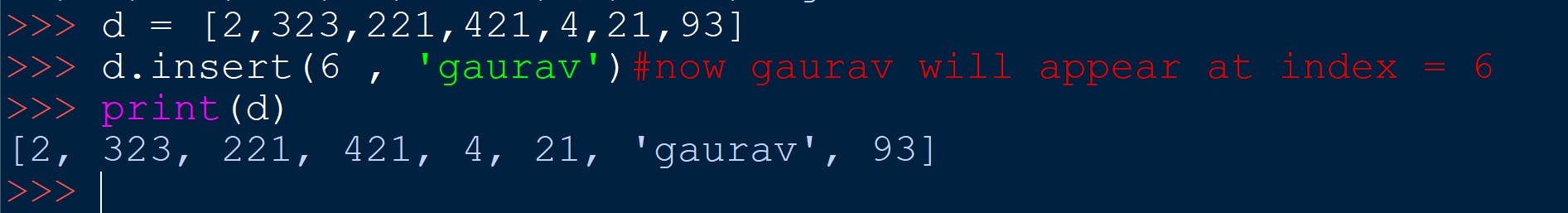
name_of_list.insert(x,y)
It adds y at index x .
name_of_list.pop(x)
It deletes the element at index = x and returns it's value.
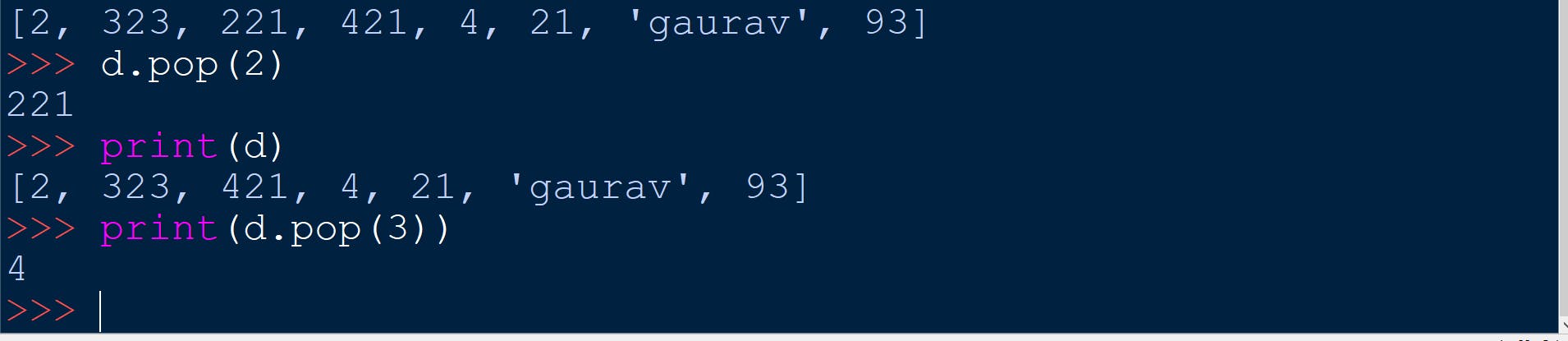
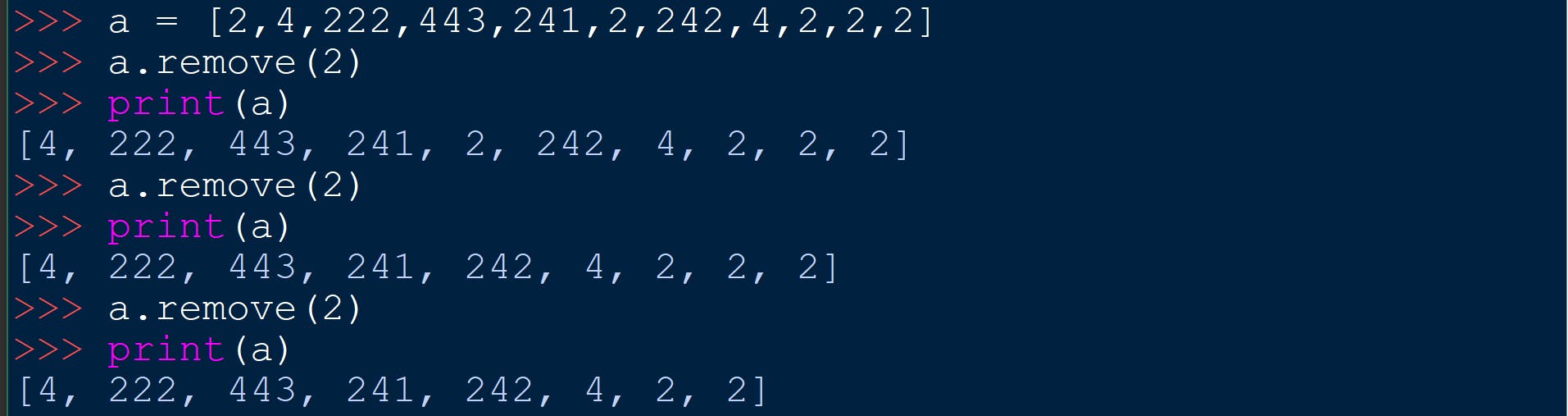
name_of_list.remove(x)
It will remove the element x from the list.
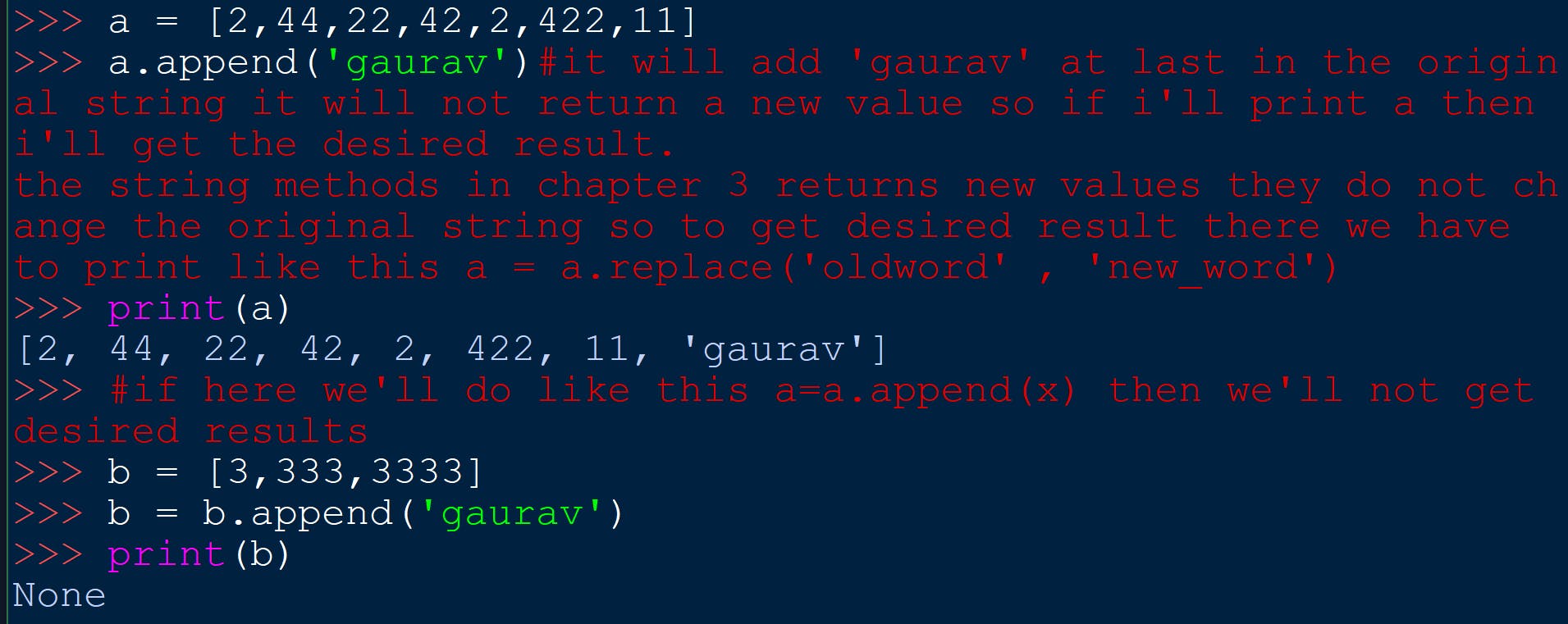
ALL LIST METHODS CHANGE THE ORIGINAL STRING THEY DO NOT RETURN NEW VALUES.
You can see this in the example below
TUPLES
TUPLES ARE IMMUTABLE DATATYPE IN PYTHON. Tuples are just like lists but the only difference is that tuples are immutable but lists are mutable datatype in python .
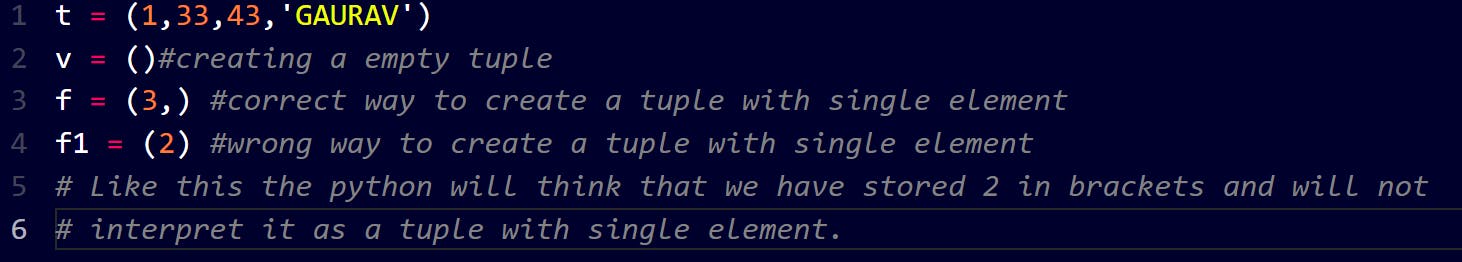
HOW TO CREATE A TUPLE
TUPLE METHODS
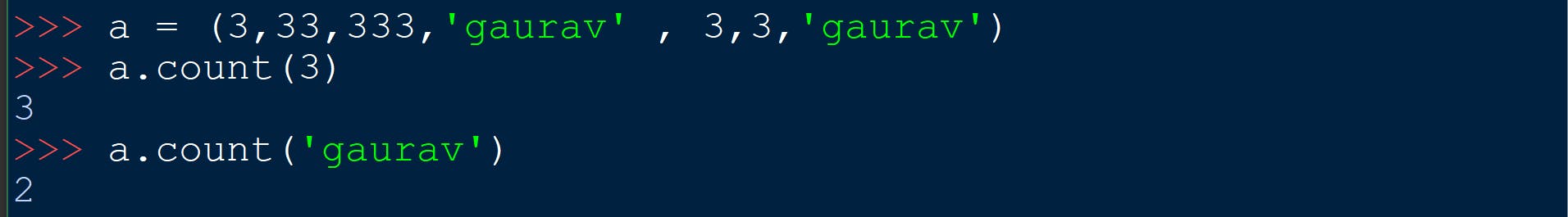
name_of_tuple.count(x)
It counts no of times x occurs in the given tuple.
name_of_tuple.index(x)
It will return the index of first occurence of x in the given string.

We can access and slice the elements of a tuple the same way we do for strings and lists
